What is Radon?
Radon comes from the natural breakdown of uranium in soil, rock and water. The release of this radioactive gas enters the air you breathe, causing a potential health risk to you and your family. Radon gas can be found just about anywhere. It can get into any type of building — homes, offices, and schools — and build up to high levels.
What you should know about Radon
Radon is a cancer-causing radioactive gas. You cannot see radon and you cannot smell it or taste it, but it may be a problem in your home. This is because when you breathe radon-containing air, you increase your risk of getting lung cancer. In fact, the Surgeon General has warned that radon is the second leading cause of lung cancer.
You should test for radon. Testing is the only way to find out about your home’s radon level. The EPA and the Surgeon General recommend testing of all homes for radon.
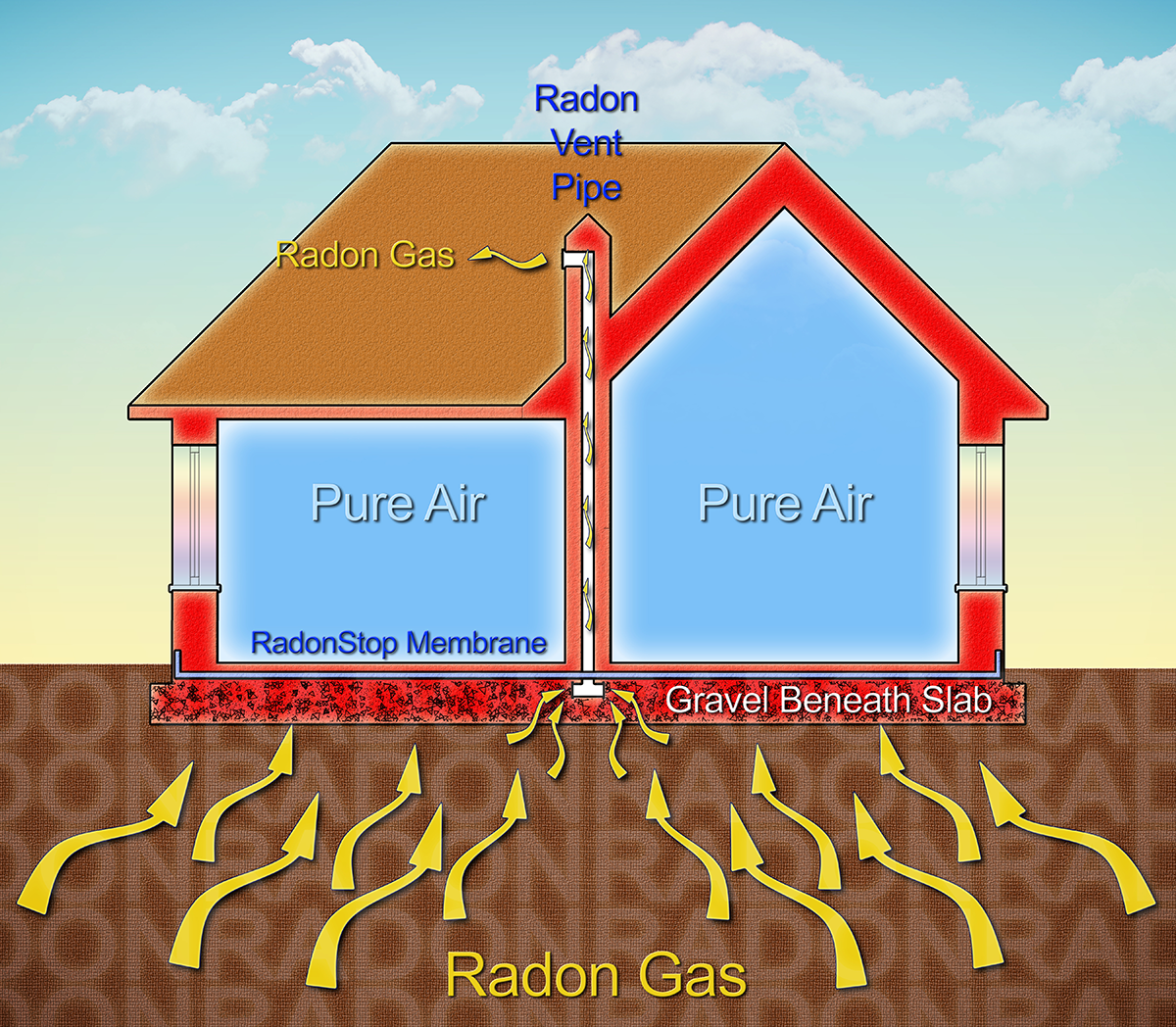
If you find that you have high radon levels, there are ways to fix a radon problem. Even very high levels can be reduced to acceptable levels with the installation of a permanent radon mitigation system that creates a negative pressure under your crawlspace or basement floor and channels the radon gas harmlessly to the outdoors.
If you are buying a home, EPA recommends that you obtain the radon level in the home you are considering buying. An EPA publication The Home Buyer’s and Seller’s Guide to Radon is available here.
If elevated levels are found it is recommended that these levels be reduced. In most cases, a professional can accomplish this at reasonable cost with a mitigation system that adheres to the EPA’s approved methods for reduction of radon in a residential structure.
Radon Testing
Our testing follows all national EPA guidelines for real estate transactions. Testing includes placing the radon monitor, the additional trip to the property to collect the test equipment, laboratory processing fees, and a final written report that details the hourly readings in relation to the temperature and barometric pressure. All radon testing requires a minimum sampling period of 48 hours. Please factor this time into your real estate transaction, and we will do our very best to accommodate any pressing contingency periods.
How Does Radon Enter the Home?
Potential Entry Points:
1. Cavities inside walls
2. Cracks in solid floors
3. Construction Joints
4. Cracks in walls
5. The water supply
6. Gaps in suspended floors
7. Gaps around service pipes
Typically the air pressure inside your home is lower than the pressure in the soil around your home’s foundation. Due to this difference, your house acts like a vacuum, drawing radon gas in through foundation cracks and other openings of your home.
But even very high levels of radon can be reduced to acceptable levels with the installation of a permanent radon mitigation system. The system, (employing PVC piping, a fan installed in-line with the piping, and sealants for cracks and openings) creates a negative pressure in the crawlspace or under your basement floor and channels the radon gas harmlessly to the outdoors instead of into your home.
What are the Risk Factors?
The Surgeon General, the Centers for Disease Control, and the EPA have all agreed that continued exposure to Radon gas can cause lung cancer. In fact, their unified position on the matter is that ALL homes should be tested for radon gas exposure, and all homes testing over 4 pCi/L should be fixed.
For More Radon Information:
Consumer’s Guide To Radon Reduction
Have you been informed your home has high levels of radon? Here is a great link from the EPA with answers to your questions.
